Cyberattacks: An Increasing Threat
Cybersecurity is an increasingly important issue. In 2019, cyberattacks on businesses and individuals increased in number and complexity. Cybercriminals are targeting small businesses. According to CNBC.com, more than half of small businesses experienced a breach last year. On average, the attacks cost businesses $200,000 with many going out of business.1
Criminals not only attack businesses, but also individuals. Rumors circulated that the Saudi Prince sent a video containing malware to Jeff Bezos’s phone through WhatsApp to track his phone activities.2
Because of the serious threat that cyberattacks represent, Nucleus Computer decided to write about where we see things going this year.
Cybersecurity Threat 1: Mobile Devices Will be Targeted
Typically, criminals look for weaknesses in any business. Because companies usually have some protections in place on their employees’ computers (servers), but not as much on their mobile devices, criminals will increasingly attack them.
Many companies adopt bring your own device (BYOD) policies for employees, which leads to even more security holes. Once the criminals hack a mobile device, they can access the entire office network.3

Because there are so many smartphones in the world (about 3.5 billion)4, criminals will target them more often. Besides this, they have a number of ways to attack smartphones, including through email, apps and texts. All of these factors make them a very attractive target.
Cybersecurity Threat 2: IoT Will be Targeted
What is IoT (Internet of Things)? This term refers to all of the devices connected to the Internet, including computers, tablets and smartphones. Also, IoT includes smart speakers (Amazon Echo, Google Home, etc.), smart TVs, security systems and cameras, appliances, smart watches and other items.
Because of the huge growth in the number of IoT devices, cybercriminals have a large target market. According to one source, there will be about 75 million IoT devices by 2025.5 Kaspersky, the cybersecurity firm, found 105 million attacks in the first half of 2019, compared to the same time period in 2018.6
Because manufacturers rush these devices to market, they do not provide them with sufficient security protection. Criminals take advantage of this by sending malware to them or using them to access other devices on the same network.
Some researchers hacked into smart devices using a laser. Please check out the following video:
Threat 3: Cloud Providers Will be Targeted
In 2019, businesses and individuals moved their files and software computing needs to the cloud. They use services like Microsoft Office 365 and Azure and Amazon Web Services. Because of this, there is no longer a need for a lot of hardware onsite, including servers.

Because of this change, cybercriminals will increasingly launch attacks on cloud providers, including online backup companies. This will make it important for businesses and people to research the providers’ security practices. Do they have data stored in several different locations? What encryption does the provider use?
Threat 4: Ransomware Attacks Become More Targeted
In the first quarter 2019, ransomware attacks grew by 118% and doubled for the entire year.7 Ransomware is malware which is installed on computers and devices. Typically, it will scramble documents and files and generate a popup demanding payment to unscramble them. Usually, the popup provides specific payment instructions, requesting payment in bitcoin, because the transaction remains anonymous.
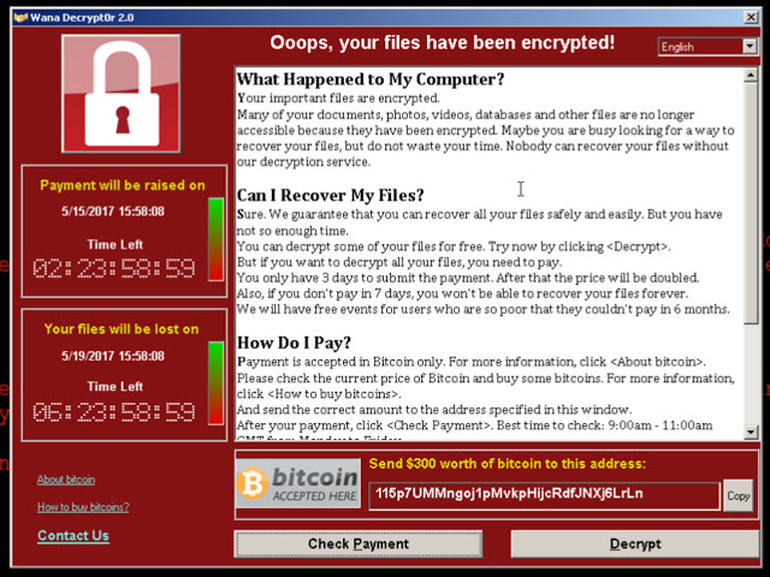
In 2019, ransomware attacks hit local governments, healthcare providers, hospital systems, dental practices, banks and corporations. In 2020, we expect this trend to continue. Because larger businesses have stronger security defenses, we expect that criminals will increasingly go after small businesses, which typically don’t have the financial resources to invest in cybersecurity.
Also, we expect these attacks to be well planned out as criminals observe businesses’ activities and systems for a while, before launching an attack. Finally, we expect the ransomware attacks to go after specific company files, like backups. This will make businesses very vulnerable.
In addition, attacks will increase on individuals, especially high net worth ones. These attacks are highly profitable and quicker, because the target is one person and not a large corporation with its bureaucracies.
Threat 5: Cybercriminals Will use Artificial Intelligence
In the past few years, the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI) have grown dramatically. Many companies, like Alphabet, Apple and Tesla, are developing self-driving cars, which improve through learning.

Companies incorporate Artificial Intelligence in their cybersecurity defense systems. While AI can add to companies’ security, many criminals observe these defense systems to determine their patterns and weaknesses. Then, they craft attacks which go after their specific holes.
We expect this trend to continue and for cybercriminals to increasingly use Artificial Intelligence and automation to guide their attacks. At one time, they will launch several different types of attacks. Then, they will tweak their campaigns based on continuous feedback on the results.
In conclusion, we hope this article has been useful and informative. If you have any questions about this topic or would like a free IT consult, please feel free to contact Nucleus Computer Services at our Contact Us page.
References:
1 CNBC.com “Cyberattacks now cost companies $200,000 on average, putting many out of business” Link to Site
2 Technewsworld.com “Saudi Hack of Bezos’ Phone Shines Bright Light on Security Challenges” Link to Site
3 Threatpost.com “2020 Cybersecurity Trends to Watch” Link to Site
4 Bankmycell.com “How Many Smart Phones are in the World? ” Link to Site
5 Statista.com “Internet of Things (IoT) connected devices installed base worldwide from 2015 to 2025” Link to Site
6 USA.Kaspersky.com “Kaspersky Reports More Than 100 Million Attacks Hit Smart Devices in H1 2019” Link to Site
7 HealthITSecurity.com “Ransomware Attacks Double in 2019, Brute-Force Attempts Increase” Link to Site